Data temperature management with BW4/HANA (Data Tiering Optimization)
One of the greatest strengths of SAP HANA is the in-memory storage of data. This allows, among other things, to strongly improve the time of the treatments (one speaks about Performance of reporting x100 and performance of loading x10 according to SAP).
But this strength does not come without its drawbacks: the infrastructure costs for a HANA system are high compared to a traditional database, particularly because of the very high memory (RAM) requirements. It is therefore crucial to anticipate and control the growth of the size of the database, particularly with a view to reducing infrastructure and licensing costs.
SAP provides tools to manage this data and its footprint on the infrastructure. In this article, we will show how to manage this on a BW/4HANA system.
The concept of multi-temperature data
The concept of multi-temperature consists in classifying the data loaded on the database according to their usage values: the more recent and frequently queried the data is, the more valuable it will be and vice versa.
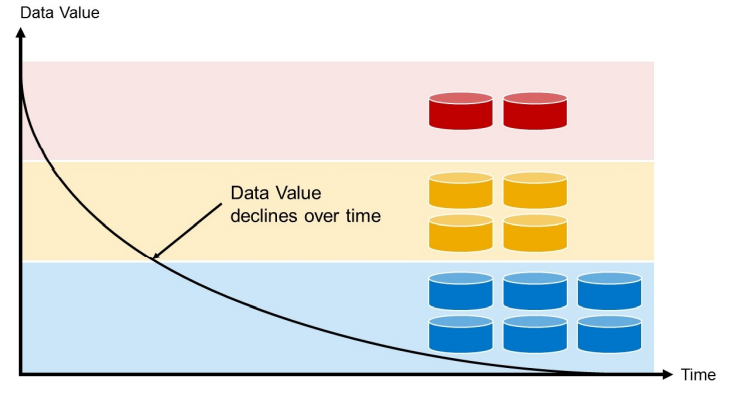
Relationship between data value and time
- hot data : frequent access to data => high value
- warm data : less frequent access => average value
- cold data: one-time access => low value
Depending on the temperature, SAP HANA offers 3 locations to store data
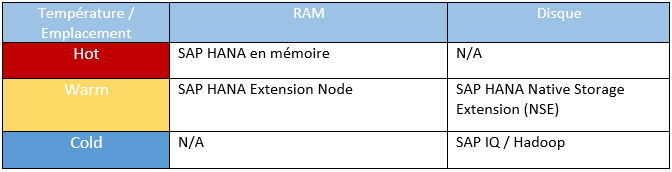
- Standard level (HOT): data is stored in main memory. SAP HANA sizing recommendations recommend a ½ ratio of stored data to available space. That is, the data should occupy 50% of the available memory space.
- Extension Level (WARM): Depending on the hardware architecture, data is stored either on SAP HANA Extension Node or on SAP HANA Native Storage Extension (NSE).
-
- SAP HANA Extension Node: SAP HANA Extension Nodes allow you to push this limitation to 200% (2 times the data size of the memory space).
- SAP HANA NSE: As of SAP BW/4HANA 2.0 SP04, SAP HANA NSE brings a new approach to store "WARM" data based on a hard drive location in SAP HANA. For more information on this topic: SAP HANA Native Storage Extension (NSE) | Q&A : Questions / Answers (bilinksolutions.com)
- External level (COLD): the data is stored in a system external to SAP HANA, either SAP IQ or Hadoop Cluster
Configuration of the data temperature
Partitioning
On SAP BW4/HANA, the aDSO is the preferred Infoprovider for persisting transactional data. This is why the data temperature is set at the level of this object.
An important concept to understand when setting up Data Tiering Optimization (DTO) is the physical partitioning of the aDSO.
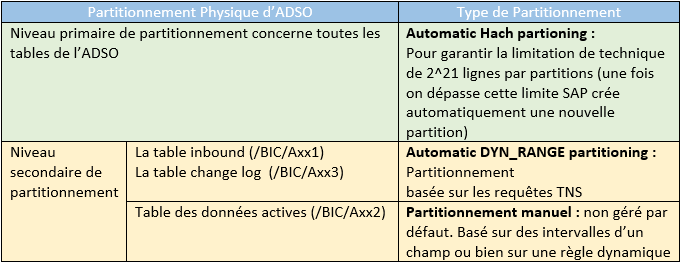
This is the third type of partitioning that allows the implementation of data temperature management.
There are two types of manual partitioning:
Static: based on an aDSO object or field to define fixed intervals (SAP recommends using a key InfoObject as a partitioning object).
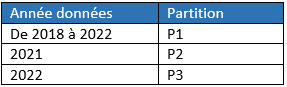
Dynamic: usually based on an InfoObject of type time Caracteristic (0calday, 0calyear...) or of a derived type such as Partition Object. The dynamic type is more flexible than the static one.
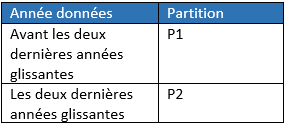
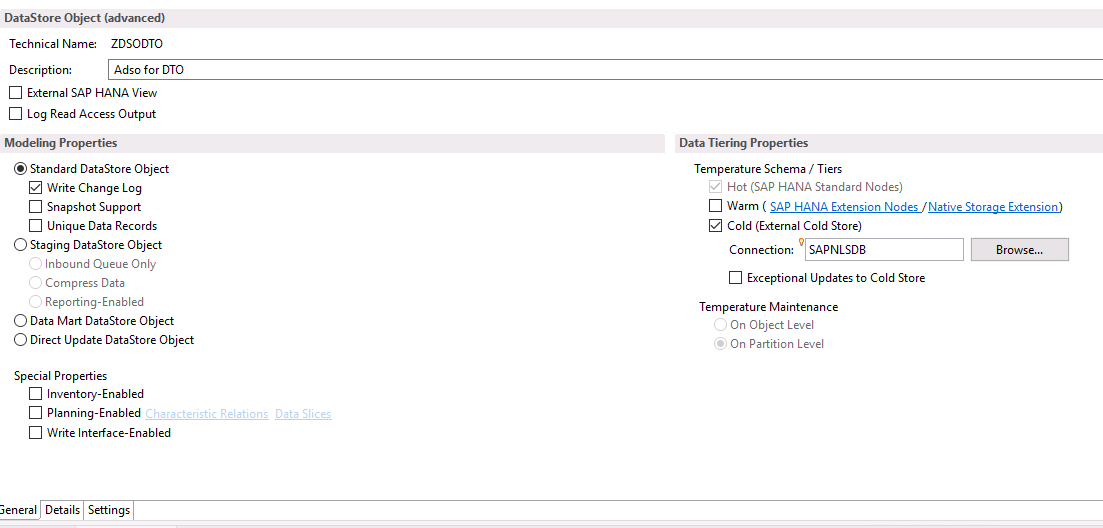
The general settings for DTO are made in the Data Tiering properties section of the aDSO General screen:
Screen shot of SAP software
Object level: All data in the table are moved (not possible with the cold setting)
Partition level: Each partition is managed independently.
In the following section we will focus on the DTO at the static partition level.
Example of a DTO configuration on an aDSO:
Configuration of the aDSO
For our example, we set this up: we select the three temperatures to manage the data temperature on the aDSO.
Prerequisites
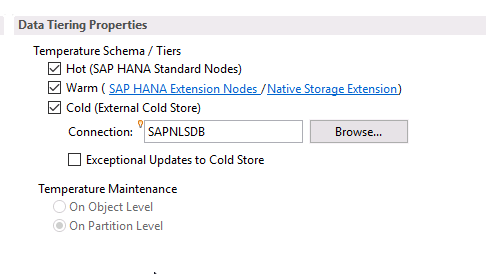
To be able to configure the cold temperature, you must first have configured the parameters of the external database (in our case SAP IQ).
Screen shot of SAP software
And therefore the temperature is only possible at the partition level (because cold is selected).
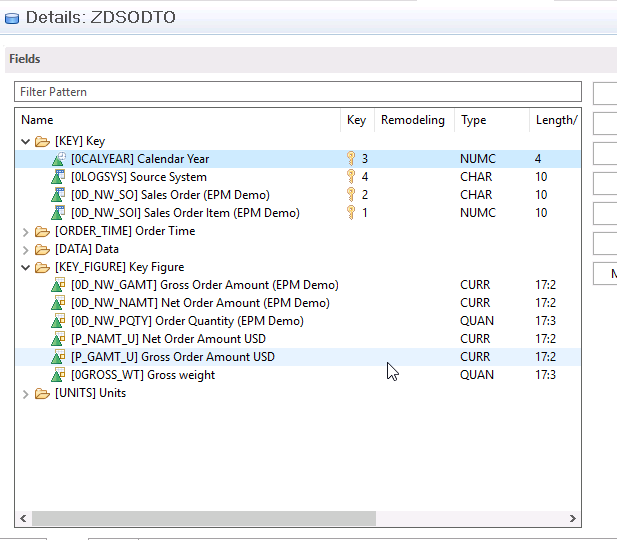
Here is the diagram of our aDSO:
Screen shot of SAP software
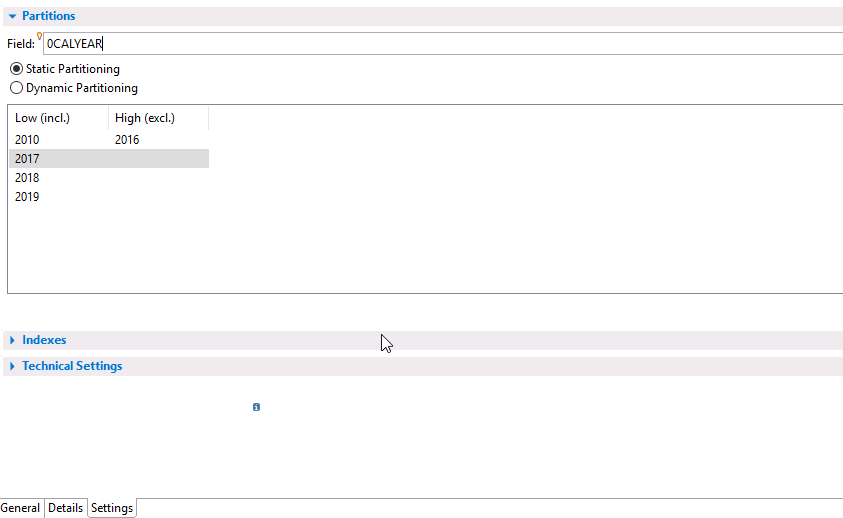
On the Settings tab we define the partitions as follows: we have selected static partitioning based on the 0CALYEAR field:
We want to manage four partitions, each corresponding to intervals of years.
Screen shot of SAP software
Before the data temperature change, let's take a look at the tables and data in our aDSO:
For the moment we only have the standard tables.
Adso standard tables
The content of the active table :
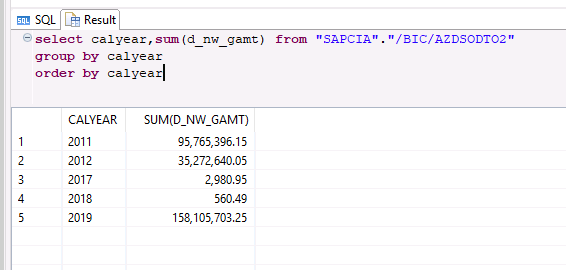
Data temperature management
There are two ways to manage data temperature:
- SAP GUI: Transaction RSOADSODTO, available since SAP BW/4HANA 1.0 SP04
- BW/4HANA cockpit: App for DataStore Objects - Manage Data Tiering, available from SAP BW/4HANA 2.0
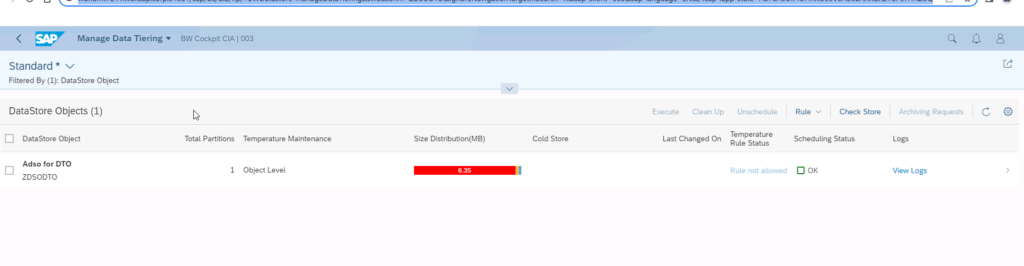
You can go directly to the cockpit configuration screen by pressing "Maintain Temperatures" on the aDSO setting screen
Screen shot of SAP software
This screen shows the distribution of the data in MB (we can see that 100% of the data are hot). Select the aDSO and press the small arrow on the right:
You can have the same configuration options via SAP GUI -> Tcode "RSOADSODTO" :
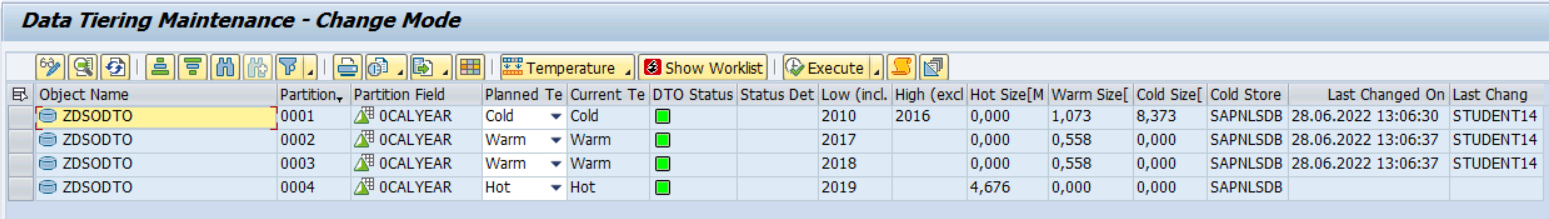
Screen shot of SAP software
You can change each partition independently. After changing the temperatures, the current temperatures have not changed, but the planned ones have taken the new values.
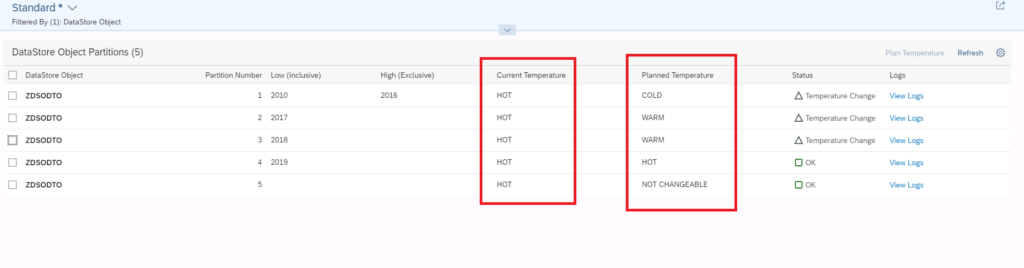
Screen shot of SAP software
Return to the previous screen and press execute. Here you can schedule a DTO job or run it immediately:
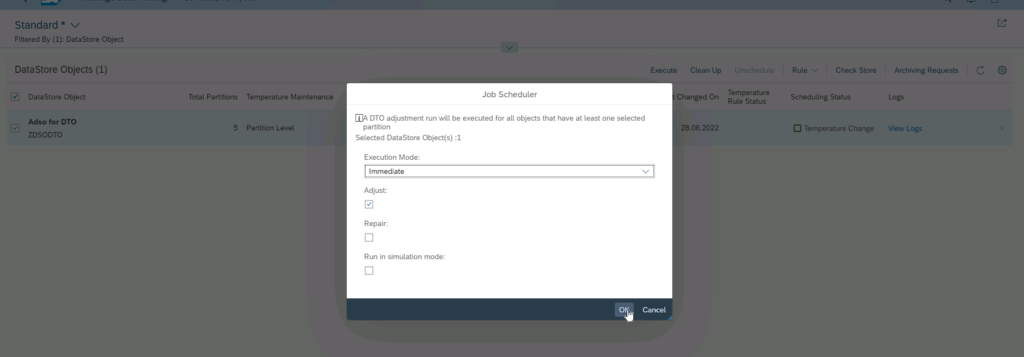
Screen shot of SAP software
After the end of the execution the data distribution has changed:
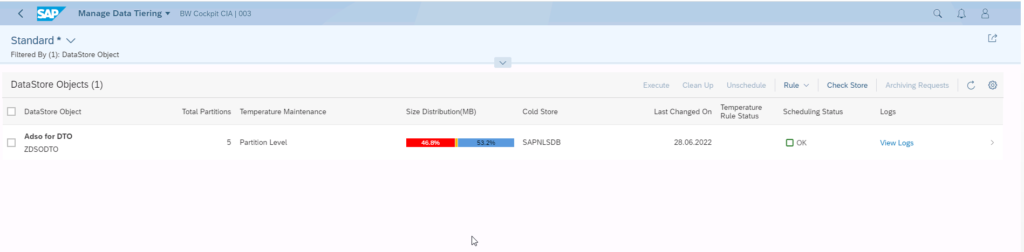
Screen shot of SAP software
You can check the details on the partition screen: the current partition has taken the planned values:
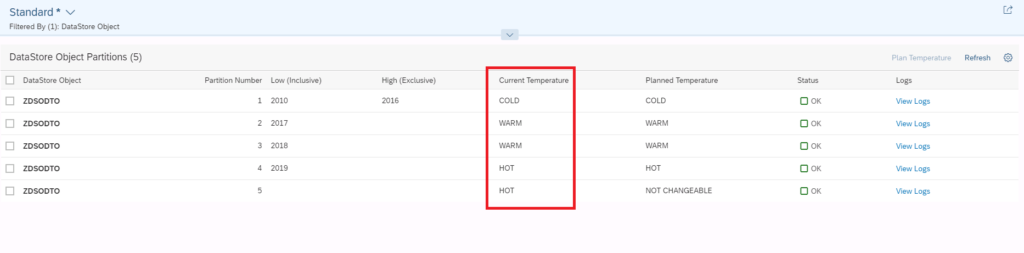
Screen shot of SAP software
The aDSO after the temperature change
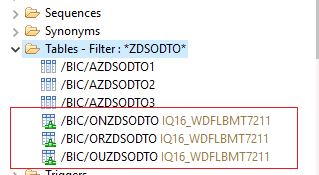
Returning to the aDSO, we notice the creation of three new external tables (on the configured external database)
Let's re-run the same query to examine the contents of the active table:
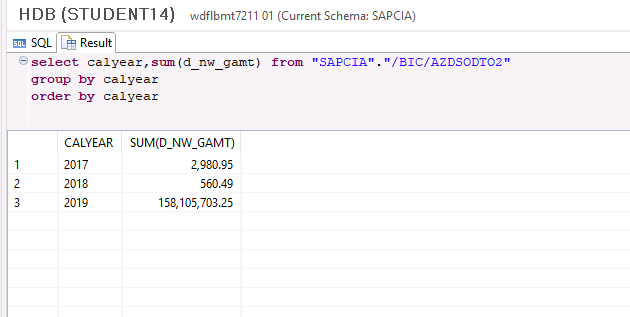
The data set as cold are no longer on the active table.
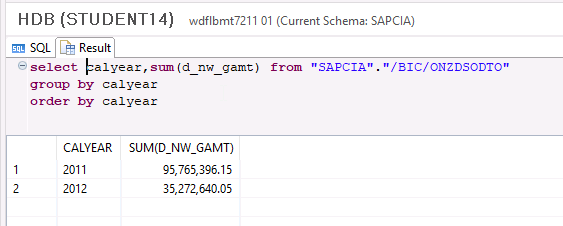
Running the same query on the "/BIC/ONZDSODTO" table shows that the cold data has been moved to it.
The other two new external tables are technical tables.
Cold data reporting
By default, data transferred to the cold level cannot be queried by reporting tools.
To change this setting:
- compositeProvider : General -> Common Runtime Properties->Cold Store Access :
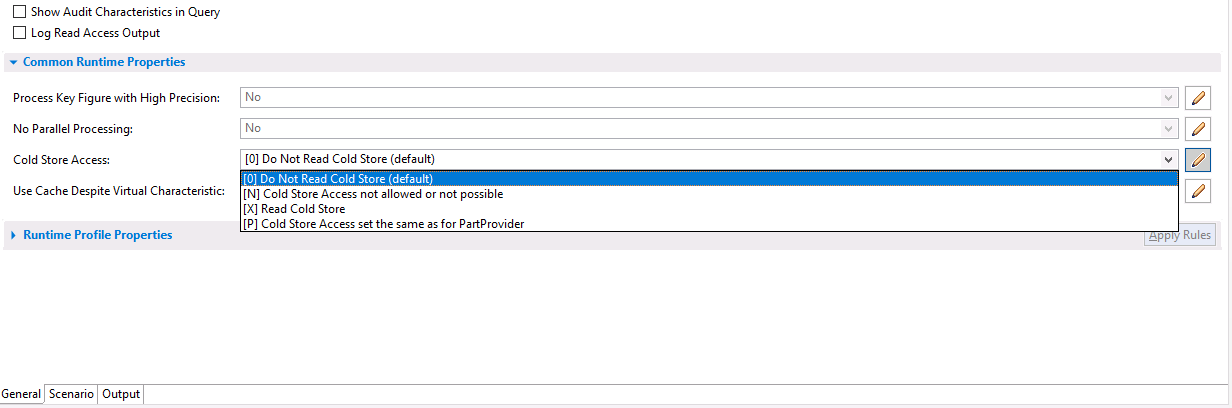
Screen shot of SAP software
- BW query: General -> Extended -> Cold Store Access:
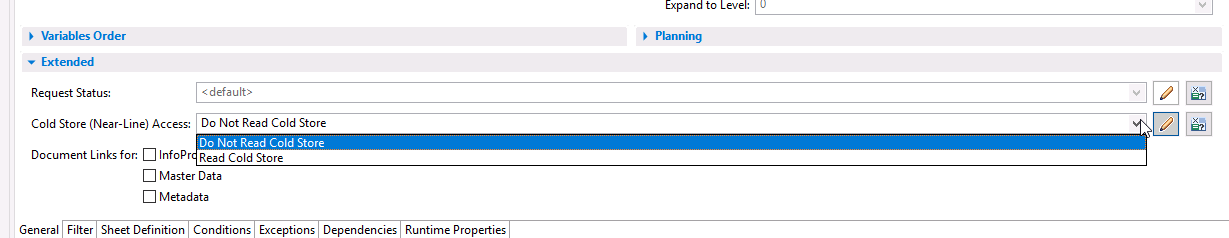
Screen shot of SAP software
Limitations
Par défaut BW ne gère pas la mise à jour des données dans la partition cold, SAP a ajouté cette fonctionnalité depuis le version BW/4HANA 2.0 SP07. Pour l’activer il faut cocher l’option « Exceptional Updates to Cold Store » sur les propriété DTO de l’aDSO. Le système crée suite à cela, à l’instar de la table /BIC/A<nom technique ADSO>1 pour les données hot et warm, une nouvelle table /BIC/A<nom technique ADSO>9 qui va gérer les mises à jour des données cold après l’activation de l’aDSO.
The size of the table / table partition is limited to 2^31 rows (about 2 billion) per partition.
A table can be divided up to 16000 partitions.
Conclusion
We have seen with a simple example how to configure the DTO on a static partitioning. There are much more complex scenarios. Especially with the use of dynamic partitioning. For example: Change the temperature of all data prior to the last 3 years to warm or cold.
In the BW/4HANA roadmap, SAP plans to add a new data temperature: Deleted. This temperature will allow to delete data from the cold partition. For more information on the subject : Deleting Data from the Cold Store | SAP Help Portal
Ayoub Arhiate
Latest articles by Ayoub Arhiate (view all)
- Data Temperature Management with BW/4HANA - September 9, 2022