Once called Data Analysis, then Data Mining, its new buzzword is Data Science or Machine Learning.
These names refer to the same thing, namely a set of techniques and tools aimed at extracting knowledge from a set of data.
For a long time reserved for specific business areas (e.g. Actuarial), and confronted with technical constraints (data volumes, processing times), it has become more democratic.
Indeed, the evolution of technologies around Data makes its use accessible to the general public:
- Big Data: allowing the manipulation of very large amounts of data
- In-Memory database: calculations and processing are reduced from hours to minutes
- Artificial intelligence: research in this area has progressed and new predictive algorithms are available.
Data Science is now available to any organisation doing BI. Most vendors offer their solutions, but it is difficult to appreciate what this technology can do for an organisation's data processing.
Raising the level of maturity of its decision-making system
Business Intelligence solutions have generally reached a certain level of maturity in companies. Those that have invested in business intelligence systems have solutions that centralise the company's information with a DataWarehouse and a reporting or Data Viz platform.
The information, harmonised and historically recorded, can be widely consulted and helps to answer the questions :
- What has happened? With reports and dashboards describing the company's activity factually
- Why / How did it happen? Using Adhoc analysis tools to explore the company's information
Once this is in place the questions can be asked:
- What will happen?
- What should be done?
These questions can be answered thanks to the mass of information stored in the Datawarehouse and in the Big Data databases, but they are difficult to exploit by an analyst. This requires time and a global knowledge of the company's information.
The challenge of data science is to accelerate this process and to make it accessible to any employee in the company.
Data Science solutions support analysis through various approaches and levels of sophistication:
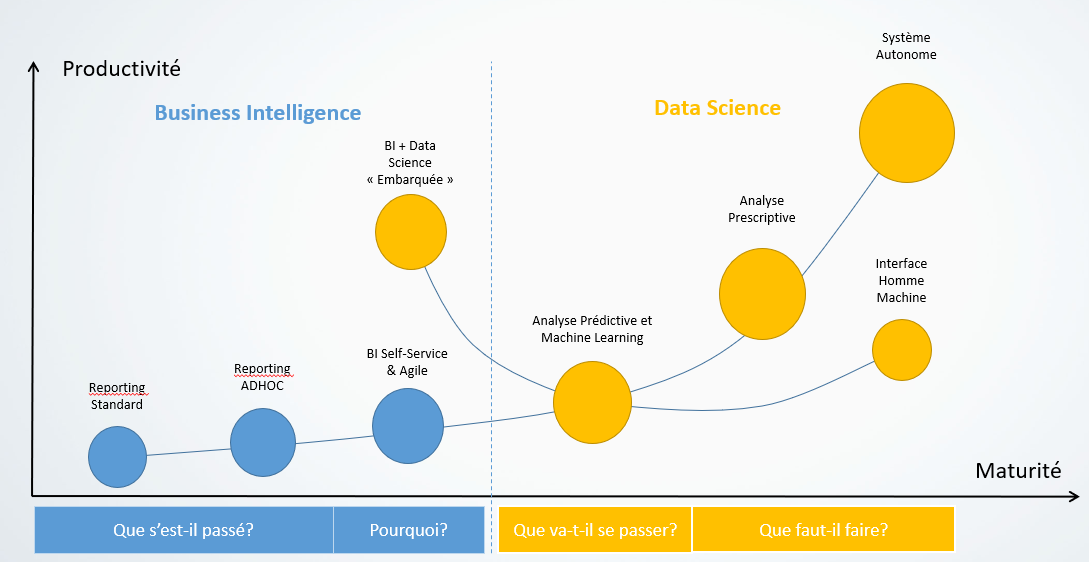
Data Science: analysis through various approaches and levels of sophistication
Creating a Predictive or Machine Learning Model
This use case is the most commonly used. The aim is to predict the value of an indicator or the occurrence of an event. To do this, a dataset is prepared that best describes what is to be predicted. When there is sufficient history and fields describing reality, statistical functions can be applied to generate a predictive model. This model is then applied to new data to make predictions.
For example, a widely used model is Classification. It allows correlations to be established between fields in a dataset and an indicator. This gives a list of the fields that most influence an indicator. By applying this model to new data, it will predict the value of the indicator based on the other fields.
This type of analysis is now automated with today's Data Science tools. A user familiar with data science concepts can generate and apply models with a few clicks. SAP offers products for this purpose with SAP Predictive Analytics and SAP Analytics Cloud.
These models can be incorporated into a data warehouse to automate predictions. SAP also offers libraries of predictive functions with its HANA platform.
Embedded BI and Data Science
SAP Analytics Cloud offers predictive analytics embedded in reports and dashboards. Predictive formulas can then be applied on the fly to derive insights from report data.
For example, you can see which fields contribute to an indicator. One can also run "what if" scenarios, to see which parameters to change to improve an indicator.
Training Data Science Citizens
With new Data Science products simplifying its use in companies, there will be more and more potential consumers of predictive information. This user profile, aware of Data Science issues, will have to be able to produce a predictive model and draw the right analyses from it. These Data Science Citizens will be able to work with Data Scientists, experts in the field, on more complex projects requiring models better adapted to their needs than those produced automatically.
They will be able to launch predictive topics within their teams and departments, and call on the experts to industrialise or improve their models.
SAP offers this synergy with SAP Predictive Analytics and Sap Analytics Cloud.
Data Science Citizen can make their predictions assisted by the tool, while Data Scientists can develop their own models.
An innovation axis for your BI system
In conclusion, adopting a Data Science solution opens up opportunities to leverage an organisation's stored information.
Data science tools and concepts are now available to analysts who are "uninitiated" in this field. Each team can start an analysis to extract information from their data.
It is also a continuation of investments made in a modern data warehouse (e.g. SAP HANA) or a Big Data database. Data Science analysis processes benefit directly from these technologies.
Philippe Dobrowlanski
Latest articles by Philippe Dobrowlanski (view all)
- New SAP BI Platform 4.3 Release - Web Intelligence, Cloud - Are We Ready? - March 30, 2020
- What to do with data science today? - 19 September 2018
- Modernising your business intelligence system with SAP - 17 May 2017
